Study Program Learning Outcomes
Code | Program Learning Outcomes |
| General Competencies |
PLO 1
| Able to show religious attitudes, humanity, love for the homeland, nationalism, internalize the spirit of independence, responsibility, and entrepreneurship. |
PLO 2
| Able to demonstrate excellence, honesty, competitiveness, leadership, and have social sensitivity towards society and the environment. |
| PLO 3 | Able to demonstrate performance independently or as part of a team in a professional and measurable manner by applying interdisciplinary knowledge and skills, critical thinking, and creatively in the context of being a lifelong learner. |
| Special Competencies |
| PLO 4 | Understand the basic principles of science and mathematics for solving various chemical problems. |
PLO 5
| Able to master knowledge of chemistry (organic, inorganic, analytical, physical and biochemical chemistry) which includes structure, properties, function, change, energy and dynamics, identification, separation, characterization, transformation, and synthesis of micromolecular chemicals and their application. |
PLO 6
| Understand concepts and applications in the field of biosciences and materials chemistry to solve problems in the field of chemistry and its applications. |
PLO 7
| Understand operational knowledge about functions, how to operate chemical instruments, as well as analysis of data and information from these instruments. |
PLO 8
| Understand work safety, ethics, environmental issues and policies related to the chemical field. |
PLO 9
| Able to communicate ideas, scientific research results clearly in oral or written format to scientists and the wider community. |
| PLO 10 | Able to carry out laboratory and research work by paying attention to the safety and security of laboratory work and applying responsible scientific behavior. |
PLO 11
| Able to obtain, process, interpret, and evaluate scientific data and produce conclusions by considering scientific and technological aspects as well as scientific ethics. |
| PLO 12 | Able to solve science and technology problems in chemistry independently based on relevant scientific methodologies. |
Curriculum Structure
The curriculum structure of the Chemistry Study Program consists of general subject groups (MKU), with a range of 144-146 credit units. To become a chemistry graduate, students are required to write a final project (thesis) based on research in the field of chemistry.
| No | GROUP | Status | Course Credits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | General Course | Compulsory | 14 |
| 2 | Faculty Characteristics Course | Compulsory | 1 |
| 3 | Compulsory Courses Characteristics of Study Programs | Compulsory | 105 |
| 4 | Elective Courses | Elective | 24 |
| Total | 144 |
The difference between the regular program and the MBKM is the elective courses taken. The provisions for the structure of elective courses for the regular program are presented in the following table:
| No | Elective Courses | Course Credits |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Outside PS in PT (minimum) | 6 |
| 2 | Outside PS outside PT (minimum) | 6 |
| 3 | In PS | 12 |
| Total | 24 |
The provisions for the structure of the MBKM Program elective courses are presented in the following table:
| No | Elective Courses | Course Credits |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Elective courses in the Study Program | 4 |
| 2 | MBKM course conversion | 20 |
| Total | 24 |
MBKM conversion course
| 1. MBKM Research Internship | MBKM Research Internships can be converted into the following courses: | Course Credits |
| a. Field Work Practice | 6 | |
| b. Professional Ethics | 3 | |
| c. Creativity and Innovation | 3 | |
| d. Communication Skills | 2 | |
| e. Problem Solving and Decision Making | 3 | |
| f. Information and Digital Literacy | 3 | |
| Total | 20 | |
| 2. MBKM Industry Internship | MBKM Industrial Internships can be converted to the following courses: | |
| a. Field Work Practice | 6 | |
| b. Professional Ethics | 3 | |
| c. Creativity and Innovation | 3 | |
| d. Communication Skills | 2 | |
| e. Problem Solving and Decision Making | 3 | |
| f. Information and Digital Literacy | 3 | |
| Total | 20 | |
| 3. Teaching Assistant for MBKM | MBKM teaching assistance activities can be converted to the following courses: | |
| a. Teaching Planning | 3 | |
| b. Teaching Methodology | 4 | |
| c. Teaching Practice | 6 | |
| d. Evaluation of Teaching Activities | 4 | |
| e. Reports and Dissemination of Teaching Results | 3 | |
| Total | 20 | |
| 4. Entrepreneur | MBKM Entrepreneurial Activities can be converted to the following courses: | |
| a. Social Entrepreneurship | 3 | |
| b. Business Ethics | 2 | |
| c. Introduction to Management and Business | 2 | |
| d. Digital Marketing | 3 | |
| e. Businessman: 1) Entrepreneurial Design and Presentation 2) Business Practice 3) Entrepreneurship Activity Report | 10 | |
| Total | 20 | |
| 5. Student Exchange 6. Developing Village/KKN 7. Humanitarian Project 8. Independent Project | Activities 5-8 MBKM can be converted into the following courses: | |
| Project Planning and Design/SI | 3 | |
| Project Management/SI | 4 | |
| Project Implementation/SI | 6 | |
| Project Data Analysis/SI | 4 | |
| Report and Dissemination of Project Results/SI | 3 | |
| Total | 20 |
Curriculum Mapping
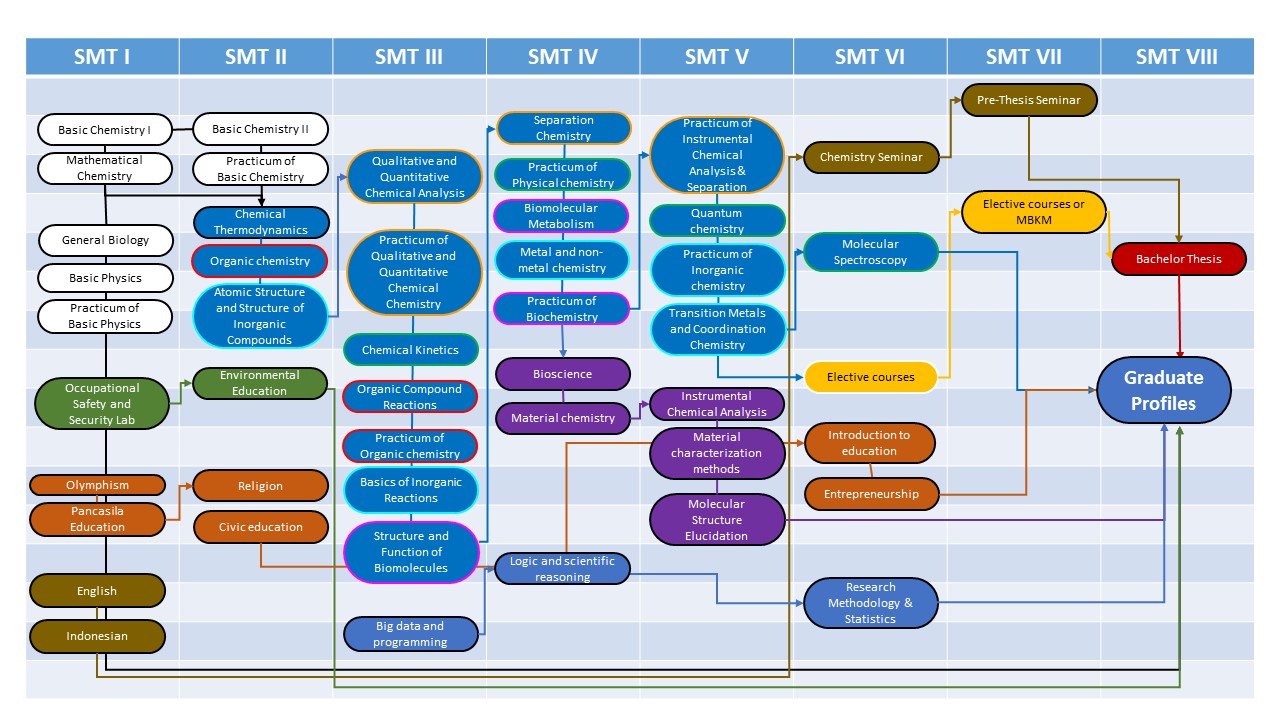
Courses Relationship to PLO

Assessment Method
The passing value of a course is based on the value of the mid-semester exam (UTS), the value of the final semester exam (UAS), and the value of both independent and structured assignments. For courses that include practicum, the assessment is added to the practicum scores. The final grade of the course is calculated based on the weighting of each assessment source. The final score is based on the following criteria:
| CAPABILITY LEVELS | GRADE | VALUE | PREDICATE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 86-100% | A | 4 | Very Good |
| 81-85% | A- | 3,7 | |
| 76-80% | B+ | 3,3 | Good |
| 71-71% | B | 3 | |
| 66-70% | B- | 2,7 | |
| 61-65% | C+ | 2,3 | Adequate |
| 56-60% | C | 2 | |
| 51-55% | C- | 1,7 | Not Pass |
| 46-50% | D | 1 | |
| <46 | E | 0 |
